HSRP Questions 3
Here you will find answers to HSRP Questions – Part 3
Question 1
Which two statements are true about the Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)? (Choose two)
A. Load sharing with HSRP is achieved by creating multiple subinterfaces on the HSRP routers.
B. Routers configured for HSRP can belong to multiple groups and multiple VLANs.
C. Load sharing with HSRP is achieved by creating HSRP groups on the HSRP routers.
D. All routers configured for HSRP load balancing must be configured with the same priority.
E. Routers configured for HSRP must belong to only one group per HSRP interface.
Answer: B C
Explanation
B is correct according to http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst3550/software/release/12.1_19_ea1/configuration/guide/swhsrp.html
To load sharing with HSRP, we can divide traffic into two HSRP groups:
+ One group assigns the active state for one switch
+ The other group assigns the active state for the other switch
The example below shows how to load sharing with HSRP:
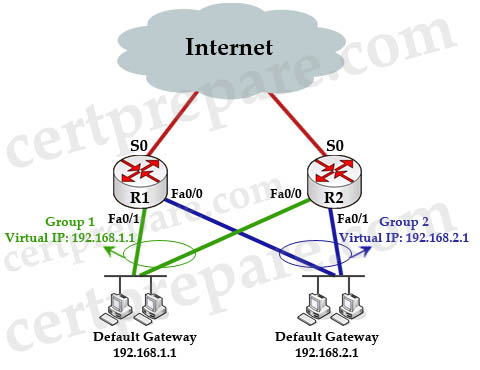
In this topology, R1 is the active router for Group 1 and is the standby router for Group 2 while R2 is the active router for Group 2 and is the standby router for Group 1. The configurations of R1 and R2 are shown below:
| R1: interface fa0/1 //Group 1 ip address 192.168.1.2 standby 1 ip 192.168.1.1 standby 1 priority 150 standby 1 preempt standby 1 track Serial 0 ! interface fa0/0 //Group 2 ip address 192.168.2.2 standby 2 ip 192.168.2.1 standby 2 priority 145 standby 2 preempt |
R2: interface fa0/1 //Group 2 ip address 192.168.2.3 standby 2 ip 192.168.2.1 standby 2 priority 150 standby 2 preempt standby 2 track Serial 0 ! interface fa0/0 //Group 1 ip address 192.168.1.3 standby 1 ip 192.168.1.1 standby 1 priority 145 standby 1 preempt |
-> C is correct.
Note: An interface can belong to multiple HSRP groups, and the same HSRP group can be applied to different interfaces -> E is not correct.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Assume that Switch_ A is active for the standby group and the standby device has only the default HSRP configuration. What conclusion is valid?
| Switch_A(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 Switch_A(config-if)# standby 1 priority 200 Switch_A(config-if)# standby 1 preempt Switch_A(config-if)# standby 1 track interface fa 1/1 Switch_A(config-if)# standby 1 ip 10.10.10.10 |
A. If port Fa1/1 on Switch_ A goes down, the standby device will take over as active.
B. If the current standby device were to have the higher priority value, it would take over the role of active for the HSRP group.
C. If port Fa1/1 on Switch_ A goes down, the new priority value for the switch would be 190.
D. If Switch_ A had the highest priority number, it would not take over as active router.
Answer: C
Explanation
By default, the standby track interface decrement is 10 so if interface fa1/1 goes down, the new priority value is 200 – 10 = 190
Question 3
Which statement best describes first-hop redundancy protocol status, given the command output in the exhibit?

A. The first-hop redundancy protocol is not configured for this interface.
B. HSRP is configured for group 10.
C. HSRP is configured for group 11.
D. VRRP is configured for group 10.
E. VRRP is configured for group 11.
F. GLBP is configured with a single AVF.
Answer: C
Explanation
The MAC address of the last IP is 0000.0c07.ac0b indicates HSRP has been configured for group 11 (0b in hexa = 11 in decimal).
Question 4
HSRP has been configured between two Company devices. What kind of message does an HSRP configured router send out every 3 seconds?
A. Retire
B. Coup
C. Resign
D. Send
E. Hello
Answer: E
Question 5
The following command was issued on a router that is being configured as the active HSRP router.
standby ip 10.2.1.1
Which statement is true about this command?
A. This command will not work because the HSRP group information is missing
B. The HSRP MAC address will be 0000.0c07.ac00
C. The HSRP MAC address will be 0000.0c07.ac01
D. The HSRP MAC address will be 0000.070c.ad01
E. This command will not work because the active parameter is missing
Answer: B
Explanation
The full syntax of the command above is:
| standby [group-number] ip [ip-address [secondary]] |
Therefore in the command “standby ip 10.2.1.1” we recognize it is using the default group-number, which is 0 -> The last two-digit hex value of HSRP MAC address should be “00”.
Question 6
What can be determined about the HSRP relationship from the displayed debug output?
| *Mar 1 00:12:16.871: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Active pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00:12:16.871: SB11: Vl11 Active router is 172.16.11.112 *Mar 1 00:12:18.619: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Vlan11, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:12:18.623: SB: Vl11 Interface up *Mar 1 00:12:18.623: SB11: Vl11 Init: a/HSRP enabled *Mar t 00:12:18.623: SB11: Vl11 Init-> Listen *Mar 1 00:12:19.619: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan1 1, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:12:19.819: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Active pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00:12:19.819: SB11: V111 Listen: h/Hello rcvd from lower pri Active router (50/172.16.11.112) *Mar 1 00:12:22.815: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Active pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00:12:22.815: SB11: Vl11 Listen: h/Hello rcvd from lower pri Active router *Mar 1 00:12:25.683: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Active pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00:12:25.683: SB11: Vl11 Listen: h/Hello rcvd from lower pri Active router (50/172.16.11.112) *Mar 1 00:12:28.623: SB11: Vl11 Listen: d/Standby timer expired (unknown) *Mar 1 00:12:28.623: SB11: Vl11 Listen-> Speak *Mar 1 00:12:28.623: SB11: Vl11 Hello out 172.16.11.111 Speak pri 100 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00:12:28.659: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Active pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00:12:28.659: SB11: Vl11 Speak h/Hello rcvd from lower pri Active router (50/172.16.11.112) *Mar 1 00:12:31.539: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Active pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00:12:31.539: SB11: Vl11 Speak h/Hello rcvd from lower pri Active router (50/172.16.11.112) *Mar 1 00:12:31.575: SB11: Vl11 Hello out 172.16.11.111 Speak pri 100 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00:12:34.491: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16 11.112 Active pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 |
A. Router 172.16.11.112 will be the active router because its HSRP priority is preferred over router 172.16.11.111
B. Router 172.16.11.111 will be the active router because its HSRP priority is preferred over router 172.16.11.112
C. The IP address 172.16.11.111 is the virtual HSRP router IP address.
D. The IP address 172.16.11.112 is the virtual HSRP router IP address.
E. The nonpreempt feature is enabled on the 172.16.11.112 router.
F. The preempt feature is not enabled on the 172.16.11.111 router.
Answer: F
Explanation
To understand the output you should learn these terms:
| Field | Description |
| SB | Abbreviation for “standby” |
| Vl11 | Interface on which a Hot Standby packet was sent or received. |
| Hello in | Hello packet received from the specified IP address. |
| Hello out | Hello packet sent from the specified IP address. |
| pri | Priority advertised in the hello packet. |
| ip address | Hot Standby group IP address advertised in the hello packet. |
| state | Transition from one state to another. |
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/debug/command/reference/db_s1.html)
From the output we learn:
| Line | Debug output | Description |
| 1 | Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Active pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 | Priority of 172.16.11.112 is 50 (its standby IP address is 172.16.11.115) |
| 2 | Active router is 172.16.11.112 | The current active router is 172.16.11.112 |
| 3 | Interface Vlan11, changed state to up | Interface Vlan11 is turned on |
| 6 | Init-> Listen | Our router changes from Init to Listen state |
| 15 | Listen-> Speak | After the standby timer expired (line 14), our router changes from Listen to Speak state |
| 16 | Hello out 172.16.11.111 Speak pri 100 ip 172.16.11.115 | Our router IP is 172.16.11.111, priority is 100 (its standby IP address is also 172.16.11.115) |
| 18 | Speak h/Hello rcvd from lower pri Active router | The Hellos received from lower priority Active router but our router does not send Coup message to take over active state |
In short, our router (172.16.11.111) changes from Init -> Listen -> Speak state. It received hellos from the active router 172.16.11.112 with lower priority but it does not send Coup message to take over active state -> It is not configured with the “preempt” command.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the “debug standby” output in the exhibit, which HSRP statement is true?
| *May 10 20:34:08.925: *SYS- 5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console *May 10 20:34:10.213: LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Vlan11, changed state to up *May 10 20:34:10.221: SB: Vl11 : Interface up *May 10 20:34:10.221: SB11: Vl11 Init: a/HSRP enabled *May 10 20:34:10.221: SB11: Vl11 Init -> Listen *May 10 20:34:11.213: LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan11 changed state to up *May 10 20:34:20.221: SB11: Vl11 Listen: c/Active timer expired (unknown) *May 10 20:34:20.221: SB11: Vl11 Listen -> Speak *May 10 20:34:20.221: SB11: Vl11 Hello out 10.10.10, 111 Speak pri 100 ip 10.10. 10.115 *May 10 20:34:28.905; SB11: Vl11 Hello out 10.10.10.111 Speak pri 100 ip 10.10. 10.115 *May 10 20:34:30.221: SB11: Vl11 Speak: d/Standby timer expired (unknown) *May 10 20:34:30.221: SB11: Vl11 Standby router is local *May 10 20:34:30.221; SB11: Vl11 Speak -> Standby *May 10 20:34:30.221; SB11: Vl11 Hello out 10.10.10.111 Standby pri 100 ip 10.10. 10.115 *May 10 20:34:30.221: SB11: Vl11 Standby: e/Active timer expired (unknown) *May 10 20:34:30.221: SB11: Vl11 Active router is local *May 10 20:34:30.221: SB11: Vl11 Standby router is unknown, was local *May 10 20:34:30.221: SB11: Vl11 Standby -> Active *May 10 20:34:30.221: %STANDBY-6- STATECHANGE: Vlan11 Group 11 state Standby -> Active *May 10 20:34:30.221: SB11: Vl11 Hello out 10.10.10.111 Active pri 100 ip 10.10. 10.115 *May 10 20:34:33.085: SB11: Vl11 Hello out 10.10.10.111 Active pri 100 ip 10.10. 10.115 |
A. DSW111 is the active router because it is the only HSRP-enabled router on that segment.
B. DSW111 is the active router because the standby timer has been incorrectly configured.
C. DSW111 is the active router because it has a lower priority on that VLAN.
D. DSW111 is the active router because it has a lower IP address on that VLAN.
E. DSW111 is the active router and is advertising the virtual IP address 10.10.10.111 on VLAN 11.
Answer: A
Explanation
From the output we learn that DSW111 moves from Init -> Listen -> Speak -> Standby -> Active and all the messages are “Hello out” (no messages are “Hello in”). This means that DSW111 is the only router sending messages in this segment.
(If you don’t know about these terms please read the explanation of Question 6)
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the debug output shown in the exhibit, which three statements about HSRP are true? (Choose three.)
| *Mar 1 00 16:43.095: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Vlan11, changed state to up *Mar 1 00 16:43.099: SB: Vl11 Interface up *Mar 1 00 16:43.099: SB11: Vl11 Init: a/HSRP enabled *Mar 1 00 16:43.099: SB11: Vl11 Init -> Listen *Mar 1 00 16:43.295: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Active pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00 16:43.295: SB11: Vl11 Active router is 172.16.11.112 *Mar 1 00 16:43.295: SB11: Vl11 Listen: h/Hello rcvd from lower pri Active router (50/172.16.11.112) *Mar 1 o o 16:43.295: SB11: Vl11 Active router is local, was 172.16.11.112 *Mar 1 00 16:43.299: %STANDBY-6-STATECHANGE: Vlan11 Group 11 state Listen -> Active *Mar 1 00 16:43.299: SB11: Vl11 Hello out 172.16.11.111 Active pri 100 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00 16:43.303: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Speak pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00 16:46.207: SB11: Vl11 Hello out 172.16.11.111 Active pri 100 ip 172.16.11.115 *Mar 1 00 16:49.095: SB11: Vl11 Hello in 172.16.11.112 Speak pri 50 ip 172.16.11.115 |
A. The router with IP address 172.16.11.111 has preempt configured.
B. The final active router is the router with IP address 172.16.11.111.
C. The router with IP address 172.16.11.112 has nonpreempt configured.
D. The priority of the router with IP address 172.16.11.112 is preferred over the router with IP address 172.16.11.111.
E. The router with IP address 172.16.11.112 is using default HSRP priority.
F. The IP address 172.16.11.115 is the virtual HSRP IP address.
Answer: A B F
Question 9

Examine the router output above. Which two items are correct? (Choose two)
A. The local IP address of Router A is 10.1.0.6.
B. The local IP address of Router A is 10.1.0.20.
C. If Ethernet 0/2 goes down, the standby router will take over.
D. When Ethernet 0/3 of RouterA comes back up, the priority will become 105.
E. Router A will assume the active state if its priority is the highest.
Answer: D E
The current state of this router is “active” and the standby router is 10.1.0.6, which makes answer A incorrect)
The IP address of the local router is not mentioned so we can’t conclude answer B. Notice that the IP 10.1.0.20 is just the virtual IP address of this HSRP group.
+ “Tracking 2 objects, 0 up” -> both Ethernet0/2 and 0/3 are currently down so the priority of RouterA was reduced from 120 to 95 (120 – 15 – 10). Therefore when Ethernet0/3 is up again, the priority of RouterA will be 95 + 10 = 105 -> D is correct.
From the line “preempt enabled” we learn this router is configured with “preempt” command so it will take over the active state if its priority is the highest -> E is correct. But a funny thing in this question is even when two interfaces are down, the priority of RouterA is still higher than the standby router so it is still the active router (the priority of standby router is 75). This also makes answer C incorrect.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the information provided in the exhibit, which two sets of procedures are best practices for Layer 2 and 3 failover alignment? (Choose two)
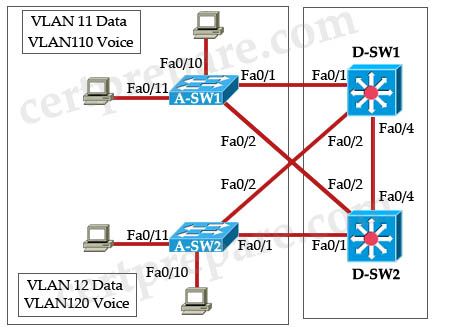
A. Configure the D-SW1 switch as the active HSRP router and the STP root for all VLANs. Configure the D-SW2 switch as the standby HSRP router and backup STP root for all VLANs.
B. Configure the D-SW1 switch as the standby HSRP router and the STP root for VLANs 11 and 110. Configure the D-SW2 switch as the standby HSRP router and the STP root for VLANs 12 and 120.
C. Configure the D-SW1 switch as the active HSRP router and the STP root for VLANs 11 and 110. Configure the D-SW2 switch as the active HSRP router and the STP root for VLANs 12 and 120.
D. Configure the D-SW2 switch as the active HSRP router and the STP root for all VLANs. Configure the D-SW1 switch as the standby HSRP router and backup STP root for all VLANs.
E. Configure the D-SW1 switch as the active HSRP router and the backup STP root for VLANs 11 and 110. Configure the D-SW2 switch as the active HSRP router and the backup STP root for VLANs 12 and 120.
F. Configure the D-SW1 switch as the standby HSRP router and the backup STP root for VLANs 12 and 120. Configure the D-SW2 switch as the standby HSRP router and the backup STP root for VLANs 11 and 110.
Answer: C F
Explanation
The “best practices for Layer 2 and 3 failover alignment” here means using load sharing of HSRP.
To load sharing with HSRP, we can divide traffic into two HSRP groups:
+ One group assigns the active state for one switch
+ The other group assigns the active state for the other switch
-> C and F are correct.
Also please read an example of HSRP load sharing in the explanation of Question 1 on this page.


