STP Questions 5
Here you will find answers to STP Questions – Part 5
Quick notes:
BPDU filtering: prevents the switch interfaces connected to end stations from sending or receiving BPDUs.
BPDU port-guard: If any BPDU is received on a port where BPDU guard is enabled, that port is put into the err-disable state immediately.
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true about the output?
| CAT1# show spanning-tree interface FastEthernet 0/1 detail Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1) of VLAN0001 is forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1. Designated root has priority 32769, address 000a.4107.7400 Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 000a.4107.7400 Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 0 Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 BPDU: sent 237, received 1 |
| CAT2# show spanning-tree interface FastEthernet 0/2 detail Port 2 (FastEthernet0/2) of VLAN0001 is blocking Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.2. Designated root has priority 32769, address 000a.4107.7400 Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 000a.4107.7400 Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 0 Timers: message age 1, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 0 BPDU: sent 1, received 242 |
| CAT3# show spanning-tree interface FastEthernet 0/1 detail Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1) of VLAN0001 is forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1. Designated root has priority 32769, address 000a.4107.7400 Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 000a.4107.7400 Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 0 Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 BPDU: sent 24, received 0 |
A. The port on switch CAT1 is forwarding and sending BPDUs correctly.
B. The port on switch CAT1 is blocking and sending BPDUs correctly.
C. The port on switch CAT2 is forwarding and receiving BPDUs correctly.
D. The port on switch CAT2 is blocking and sending BPDUs correctly.
E. The port on switch CAT3 is forwarding and receiving BPDUs correctly.
F. The port on switch CAT3 is forwarding, sending, and receiving BPDUs correctly.
Answer: A
Explanation
From the first lines of the “show” commands and the BPDU sent and received we can conclude:
CAT1 is forwarding and sending BPDUs correctly (BPDU: sent 237, received 1) but it is not receiving BPDUs.
CAT2 is blocking and receiving BPDUs correctly (BPDU: sent 1, received 242) but it is not sending BPDUs.
CAT3 is forwarding and sending BPDUs correctly (BPDU: sent 24, received 0) but it is not receiving BPDUs.
-> only answer A is correct.
Question 2
Which of the following specifications is a companion to the IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) algorithm, and warrants the use multiple spanning-trees?
A. IEEE 802.1s (MST)
B. IEEE 802.1Q (CST)
C. Cisco PVST+
D. IEEE 802.1d (STP)
Answer: A
Explanation
MST maps multiple VLANs into a spanning tree instance, with each instance having a spanning tree topology independent of other spanning tree instances. This architecture provides multiple forwarding paths for data traffic, enables load balancing, and reduces the number of STP instances required to support a large number of VLANs. MST improves the fault tolerance of the network because a failure in one instance (forwarding path) does not affect other instances (forwarding paths).
Note: RSTP is automatically turned on along with MST (the “spanning-tree mode mst” in global configuration mode will turn on both RSTP & MST)
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/configuration/guide/cli_rel_4_0_1a/MST.html)
Question 3
What two things will occur when an edge port receives a BPDU? (Choose two)
A. The port immediately transitions to the Forwarding state.
B. The switch generates a Topology Change Notification (TCN) BPDU.
C. The port immediately transitions to the err-disable state.
D. The port becomes a normal STP switch port.
Answer: B D
Explanation
The concept of edge port basically corresponds to the PortFast feature. An edge port directly transitions to the forwarding state, and skips the listening and learning stages. An edge port that receives a BPDU immediately loses edge port status and becomes a normal spanning tree port.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cfa.shtml#edge)
Question 4
Which statement is true about RSTP topology changes?
A. Only nonedge ports moving to the blocking state generate a TC BPDU.
B. Any loss of connectivity generates a TC BPDU.
C. Any change in the state of the port generates a TC BPDU.
D. Only nonedge ports moving to the forwarding state generate a TC BPDU.
E. If either an edge port or a nonedge port moves to a block state, then a TC BPDU is generated.
Answer: D
Explanation
When a Switch (Bridge) discovers topology change, it generates a TCN (Topology Change Notification) BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) and sends the TCN BPDU on its root port. The upstream Switch (Bridge) responds back the sender with TCA (Topology Change Acknowledgment) BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) and TCA (Topology Change Acknowledgment) BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit)
The upstream Switch (Bridge) (bridge which received the TCN BPDU) generates another TCN BPDU and sends out via its Root Port. The process continues until the Root Switch (Bridge) receives the TCN BPDU.
When the Root Switch (Bridge) is aware that there is a topology change in the network, it starts to send out its Configuration BPDUs with the topology change (TC) bit set. Configuration BPDUs are received by every Switch (Bridge) in the network and all bridges become aware of the network topology change.
The switch never generates a TCN when a port configured for PortFast goes up or down -> it means no TC will be created for PortFast (or Edge Port) -> D is correct.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094797.shtml)
Question 5
Which of the following conditions guarantees that a broadcast storm cannot occur?
A. a native VLAN mismatch on either side of an 802.1Q link
B. BPDU filter configured on a link to another switch
C. Spanning Tree Protocol enabled on both Layer 2 and multilayer switches
D. PortFast enabled on all access and trunk ports
Answer: C
Question 6
Which two statements are true about port BPDU Guard and BPDU filtering? (Choose two)
A. BPDU guard can be enabled globally, whereas BPDU filtering must be enabled on a per-interface basis.
B. When globally enabled, BPDU port-guard and BPDU filtering apply only to PortFast enabled ports.
C. When globally enabled. BPDU port-guard and BPDU filtering apply only to trunking-enabled ports.
D. When a BPDU is received on a BPDU port-guard enabled port, the interface goes into the err-disabled state.
E. When a BPDU is received on a BPDU filtering enabled port, the interface goes into the err-disabled state.
F. When a BPDU is received on a BPDU filtering enabled port, the interface goes into the STP blocking state.
Answer: B D
Question 7
Which of the following will generate an RSTP topology change notification?
A. an edge port that transitions to the forwarding state
B. a non-edge port that transitions to the blocking state
C. a non-edge port that transitions to the forwarding state
D. an edge port that transitions to the blocking state
E. any port that transitions to the blocking state
F. any port that transitions to the forwarding state
Answer: C
Question 8
What is the effect of configuring the following command on a switch?
| Switch(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default |
A. If BPDUs are received by a port configured for PortFast, then PortFast is disabled and the BPDUs are processed normally.
B. If BPDUs are received by a port configured for PortFast, they are ignored and none are sent.
C. If BPDUs are received by a port configured for PortFast, the port will transition to forwarding state.
D. The command will enable BPDU filtering on all ports regardless of whether they are configured for BPDU filtering at the interface level.
Answer: A
Explanation
Please read the explanation of Question 3
Question 9
Refer to the show spanning-tree mst configuration output shown in the exhibit. What should be changed in the configuration of the switch SW_2 in order for it to participate in the same MST region?
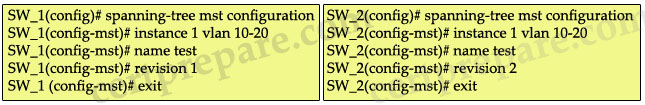
A. Switch SW_2 must be configured with the revision number of 2.
B. Switch SW_2 must be configured with a different VLAN range.
C. Switch SW_2 must be configured with the revision number of 1.
D. Switch SW_2 must be configured with a different MST name.
Answer: C
Question 10
Switch R1 has been configured with the root guard feature. What statement is true if the spanning tree enhancement Root Guard is enabled?
A. If BPDUs are not received on a non-designated port, the port is moved into the STP loop-inconsistent blocked state
B. If BPDUs are received on a PortFast enabled port, the port is disabled.
D C. If superior BPDUs are received on a designated port, the interface is placed into the root-inconsistent blocked state.
D. If inferior BPDUs are received on a root port, all blocked ports become alternate paths to the root bride.
Answer: C


